An estimated 37,000 websites are hacked on a daily basis.
And it’s not only the websites with low security measures - the IRS, Twitter, and other large corporations have faced severe repercussions because of these system hacks.
The Internet is the most popular place to conduct business; thus, hackers have become more sophisticated. The topic of website security has become a critical issue.
Download The SEO Solution: A Complete SEO Checklist for Beginners
As part of ongoing security improvement efforts, Google recently announced a system update for acknowledging websites that have (and pointing fingers at those who have not) taken the extra security measures of enabling HTTPS vs. HTTP.
Beginning January 2017, this system update within certain browsers such as Chrome and Firefox, will notify users the security connection of any website they visit. Users will be notified which sites they visit are ‘secure’ and which sites are ‘not secure’.
What is the Difference between HTTP and HTTPS?
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the system in which information (ie. any personal information, credit card numbers, or form data) is communicated between a user’s browser and a website. With HTTP, this information is exchanged in plain text. This means that if a message is intercepted on the path from a user to website by a hacker, the hacker will be able to understand and use the information that was intercepted.
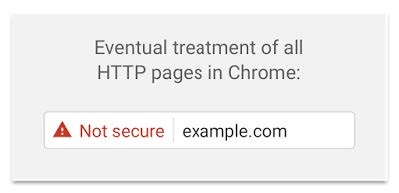
Beginning in 2017, the Chrome update will only display a ‘non-secure’ message on any web page that still operates using HTTP and requires you to input a password or credit card information. In the future, Chrome updates will display a ‘non-secure’ message as well as a hazard icon on all webpages that do not comply with HTTPS standards. Examples of these messages are below: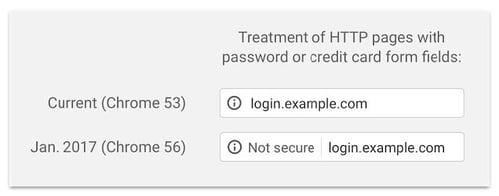
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) simply means a website has a layer of security enabled into the communication path by means of an encryption protocol. This encryption protocol is processed through a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
If a website has enabled the HTTPS protocol, users will see a secure notification within the web address bar:
![]()
But how exactly does this new ranking system affect the average website? Let’s examine the implications:
Enabling HTTPS is Important for Security
Clearly the main focus of HTTPS is security. Google’s update and announcement that the HTTPS indicator is now a ranking factor only emphasizes the importance of a secure website.
HTTPS adds a layer of security and encrypts any data transferred between user and database including:
- Filling out a form
- Entering a password
- Typing in personal information
- Adding credit card data
- And so on
This extra layer not only makes it more difficult for hackers to intercept data in the first place, but it also scrambles the information passed from user to website. In the event that the information is intercepted, the information will be rendered useless to a hacker due to the encryption protocol. Think of the encryption as a super secret code that only the specific website knows how to decode.
Enabling HTTPS also informs your users you care about their security and they can trust sharing information on your site.
Enabling HTTPS is Important for Perception
The truth is, average users will not know how to interpret notifications and icons that indicate a website is ‘not secure’.
If your website indicates a ‘not secure’ message, users may be hesitant to share any personal information. Therefore, if your website involves eCommerce or collects emails and other personal data through forms or account logins, it is especially important to enable HTTPS.
Having the secure message associated with your website will ensure users they’re in good hands, maintaining a great reputation of security and trust.
By enabling HTTPS, your website will also be known to Google as a trusted site, in turn boosting your SEO rankings.
Enabling HTTPS is Important for SEO Rankings
While the main focus of HTTPS is security, Google has also announced their algorithm will rank sites with enabled HTTPS slightly higher than those without. Their logic, when comparing similar sites, is websites with the implemented security feature are more trustworthy, making them a better reference for a user.
So, do you NEED to Enable HTTPS on your Website?
Short answer: yes.
While it is not absolutely necessary to enable HTTPS, it is a best practice. If you’re on the fence, or maybe don’t require all that much information from your visitors currently, think about the future.
If you expect growth and plan to ask web visitors more information via forms, creating accounts, or personal information, enabling HTTPS to your website now vs. later will be more impactful to your marketing efforts. You will acquire a higher rank, more web visitors, and visitors can be confident in your security.
Our free SEO checklist for beginners is another great reference for your website and marketing efforts. It provides an essential outline for what to double check to boost your ranking and remain a trusted source for your visitors.

.jpg?t=1533315998368) How-To Articles
How-To Articles Support Portal
Support Portal Webmail
Webmail Rapid Newsletter+
Rapid Newsletter+ eCMS
eCMS

 Emily is the head Content Creator. She enjoys communicating complex ideas in an easy-to-understand way.
Emily is the head Content Creator. She enjoys communicating complex ideas in an easy-to-understand way.
